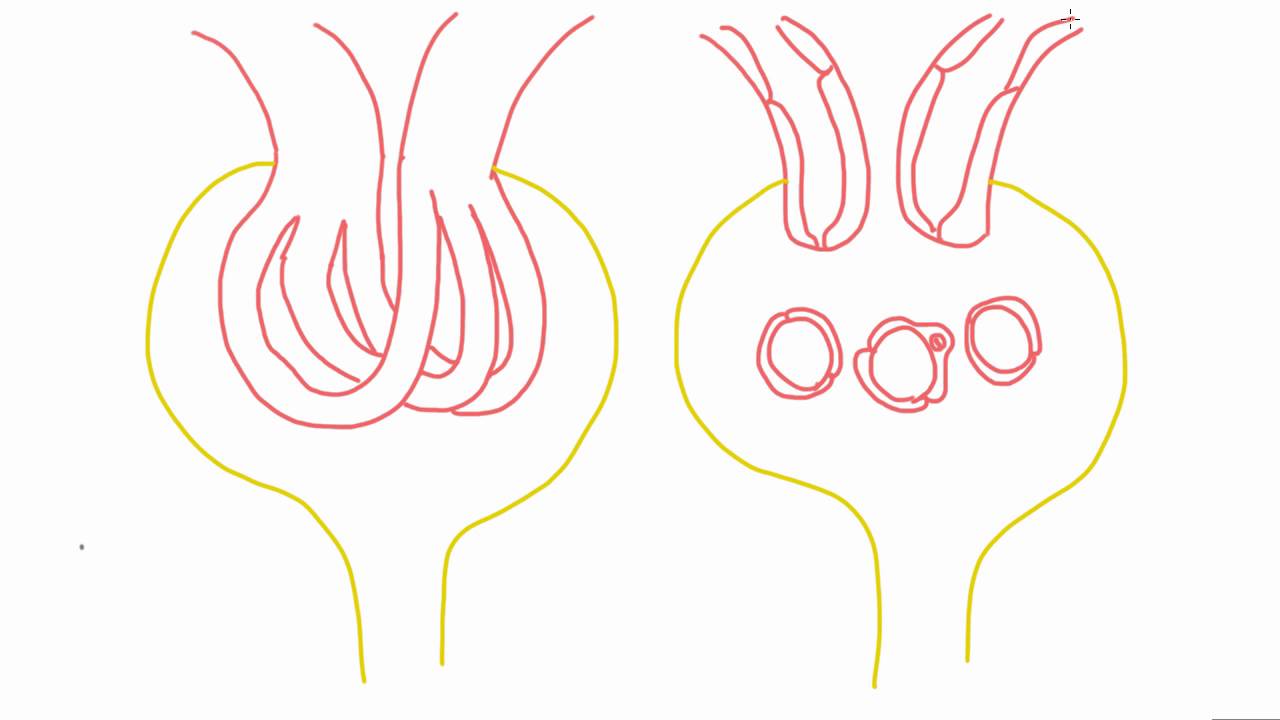
The kidneys are divided into four components: blood vessels, tubules, glomeruli and interstitium. Mesangial cells are specialized cells in the kidney. They form the glomerulus and interact very closely with podocytes and endothelial cells. Any changes in this cell type can cause changes in other cells. These specialized cells generate cytokines, endothelial cells and podocytes and influence cognate receptors. These specialized cells are secretory and play a role in glomerular development and pathological states. The research about these specialized cells is current and ongoing. The physiology of mesangial cell contraction has been studied using cultured cells.
The mesangium forms the base of the glomerular tuft. It extends underneath the endothelial cells. Also is crossed by microfilament bundles. It is thought that these bundles supply protection from hydraulic pressure. The mesangial matrix has a diverse array of proteins, including biglycan, entactin, laminin, fibronectin and fibrillin-1. Fibronectin is the most abundant. It is believed that mesangial changes are the moniker of certain glomerular diseases, such as diabetic nephropathy. It’s the thickening of the mesangial matrix that causes this. The lesion has an abnormal amount of type IV collagen in the glomerulus. Mesangial cell injury also causes systemic diseases like lupus nephritis and glomerulonephritis. Mesangial cell dysfunction from glomerulonephritis can result in end-stage renal disease. Specifically, these specialized are a stalk-like network that holds together the loops and coils of capillaries. And there are several types, too. There are immune cells similar to macrophages, and there are contractile cells. The contraction cells control capillary flow and dilation.
Despite years of research on glomeruli and mesangial cells, many questions still remain. This is because the multicellular structure is highly complicated. There is still more that needs to be studied using kidney tissues to look at the cellular interactions at the organ level. The approaches for these future studies must be adapted at the macroscopic level. Currently, lung tissue cross-sections have been used in studies. For the purpose of getting intact glomeruli, a sieving method was modified and used. Unfortunately, there are limitations to this method. A microscopical method was used to study the intact cortical slices.
While a great deal of research has been done to understand the role and importance of the kidney’s specialized cells, much of the gained knowledge has come from in vitro studies of cultured cells. Using in vivo models and ex vivo models are much more challenging. It has been suggested to use more advanced methods, such as two-photon excitation fluorescence imaging. This method could provide more detail on the specialized cells. This would allow us to answer unsolved questions and possibly rid older concepts.
